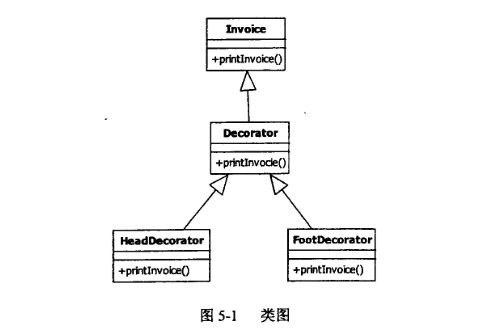
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
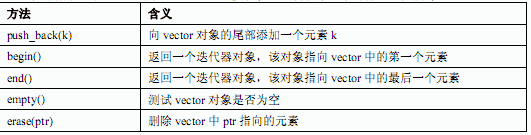
题目内容
(请给出正确答案)
●试题三 阅读下列程序说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。 【说明】 下面的
●试题三
阅读下列程序说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
下面的程序功能的功能是以行为单位对字符串按下面的条件进行排序。排序条件为:从字符串中间一分为二,右边部分按字符的ASCⅡ值降序排序,排序后左边部分与右边部分进行交换。如果原字符串长度为奇数,则最中间的字符不参加排序,字符仍放在原位置上
例如:位置:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
源字符串:h g f e a b c d
则处理后字符串:d c b a h g f e
函数ReadDat()实现从文件in.dat中读取数据(每行字符串长度均小于80),函数WriteDat()把结果dat输出到文件out.dat中。
【程序】
#include<stdio.h>
#include<siring.h>
#include<conio.h>
char dat[20][80];
void jsSort()
{
int i,j,k,strl;
char ch;
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
strl=strlen(dat[i]);
for(j= (1) ;j<strl;j++)/*对后半部分的字符串进行排序*/
for(k=j+1;k<strl;k++)
if((2) )
{
ch=dat[i][j];
dat[i][j]=dat[i][k];
dat[i][k]=ch;
}
for(j=0; (3) j++)/*前后两部分进行交换*/
{
ch=dat[i][j];
dat[i][j]=dat[i][(strl+1)/2+j];
dat[i][(strl+1)/2+j]=ch;
}
}
}
void main()
{
readDat();
jsSort();
writeDat();
}
readDat()
{
FILE*in;
int i=0;
char*p;
(4) ;
while(i<20 && fgets(dat[i],80,in)!=NULL)
{
p=strchr(dat[i],"\n");
if(p)*p=0;
i++;
}
fclose(in);
}
writeDat()
{
FILE*out;
int i;
clrscr();
out=fopen("out.dat","W");
for(i=0;i<20;i++)
{
printf("%s\n",dat[i]);
printf((5) );
}
fclose(out);
}
 如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案
如果结果不匹配,请 联系老师 获取答案


 更多“●试题三 阅读下列程序说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写…”相关的问题
更多“●试题三 阅读下列程序说明和C代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写…”相关的问题